With a strong desire to change the world with advanced materials, we are developing a wide variety of materials that include ultra-fine metal powders using chemical vapor deposition (CVD), single crystals using our original continuous-feeding Bridgman method and various complex oxides using wet synthesis and multi-stage firing techniques. In this site, we will introduce advanced ultra-fine nickel powders, iron alloy powders, PIN-PMN-PT piezoelectric single crystals for sonar, high-nickel positive electrode materials for lithium-ion secondary batteries, ZnO nanoparticles, RIPROZ®, synthetic hydrozincite and granular halloysite.
Ultra-Fine Metal Powders
Ultra-Fine Nickel Powder
Ultra-fine nickel powder is extensively used for internal electrodes of multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs). We have been conducting research and development on the advanced ultra-fine nickel powder with a consistent particle size distribution and high level of crystallinity by evolving the CVD manufacturing process. The photographs show scanning electron micrographs of nickel particles with average size from 0.1 to 0.4 micron and the figure shows their size distribution. The 0.4 micron powder is mainly used for general-purpose MLCCs and the 0.2 micron powder is used for advanced MLCCs. Both have received good reputations for these applications. The 0.1 micron powder under development will be effective for thinning and smoothing the inner electrodes of next generation MLCCs.
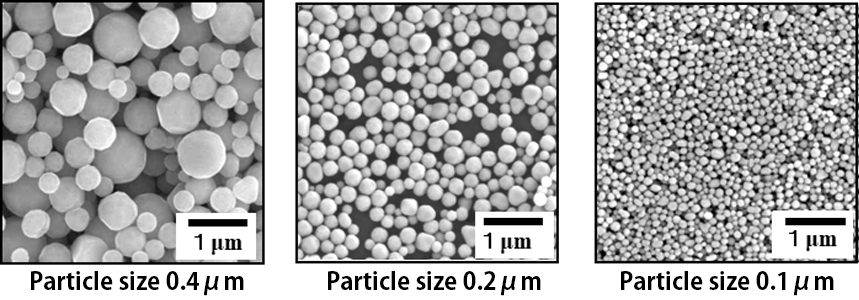
Scanning electron micrographs of 0.4, 0.2, 0.1 micron powders
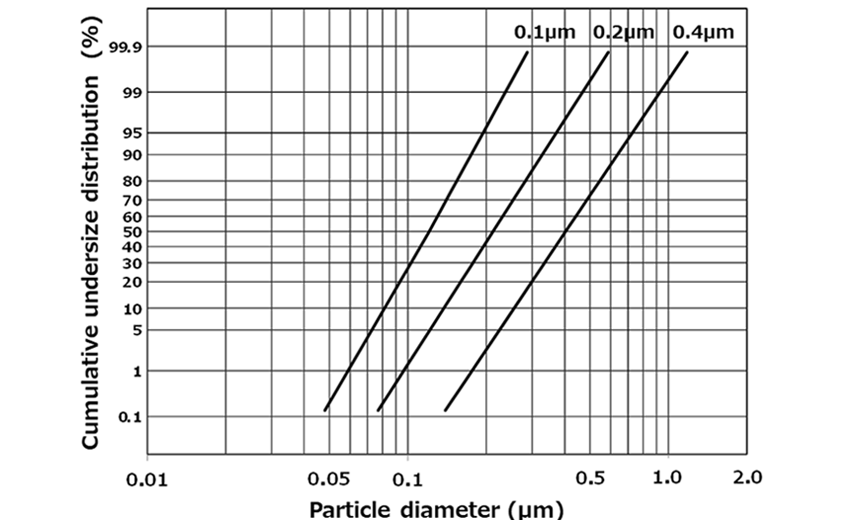
Particle size distribution of 0.4, 0.2, 0.1 micron powders
Iron Alloy Powder
Sub-micron size iron alloy powders produced by the CVD method are expected to be applied to metal power inductors and electromagnetic shielding materials.
【Expected Characteristics】
- Good DC superposition characteristics because of the iron alloy with large saturation magnetization
- Small eddy current loss at high frequency because of the sub-micron size
- Suppression of increase in coercive force due to silicon addition in fine grains
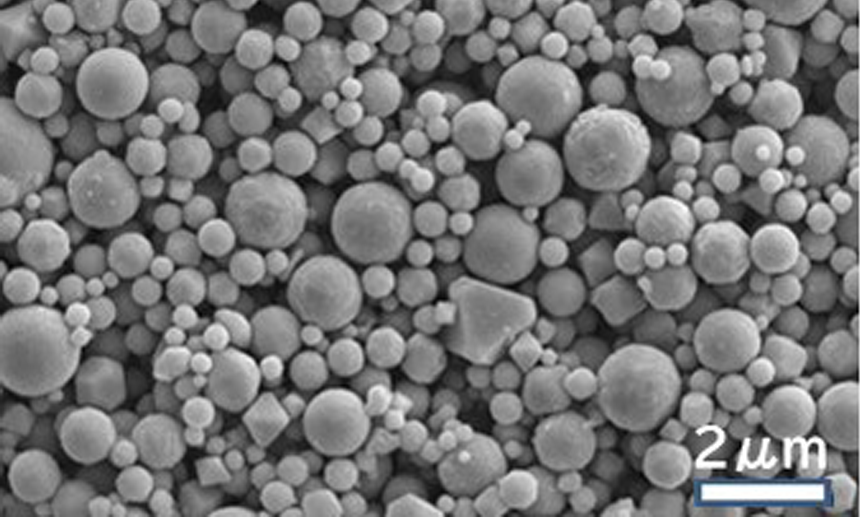
Scanning electron micrograph of Fe-8%Si-3%Cr Powder
Number base mean diameter of primary particles is 0.5 µm
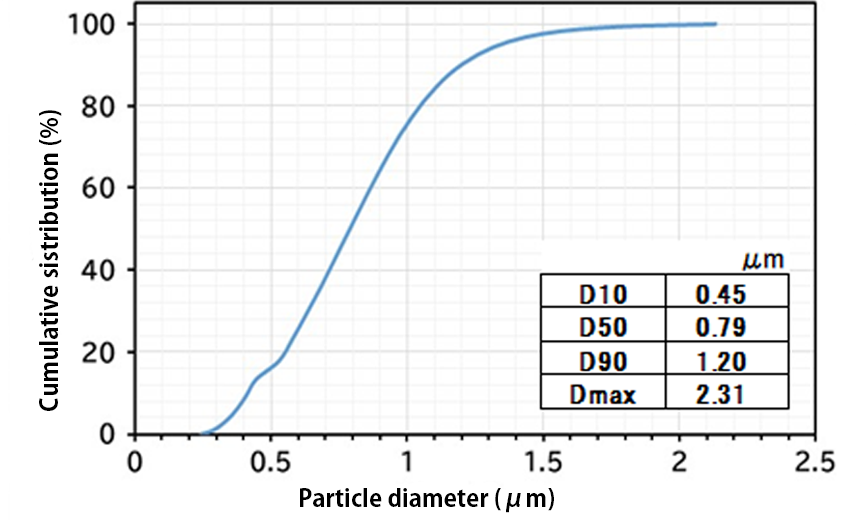
Laser diffraction particle size distribution of iron alloy powder
Ion-exchange water as solvent on volume basis
Single Crystals
High thermal stability PIN-PMN-PT single crystal
By taking advantage of the excellent compositional controllability of the continuous- feeding Bridgman method, we have improved the phase transition temperature of standard PIN-PMN-PT piezoelectric single crystals and made it possible to use them at higher temperatures. Since its phase transition compressive stress is also improved, it is expected to be a suitable material for the Langevin-type transducer used in sonar which requires high stability.
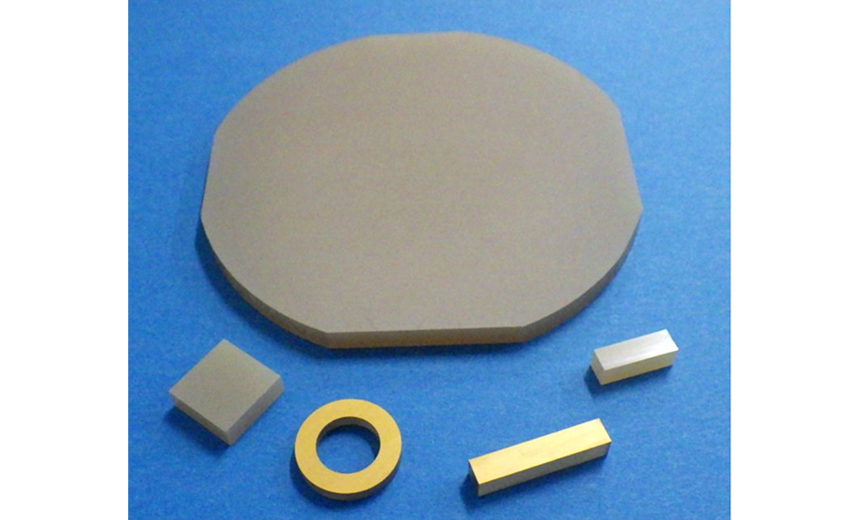
Example of high thermal stability PIN-PMN-PT single crystal processing
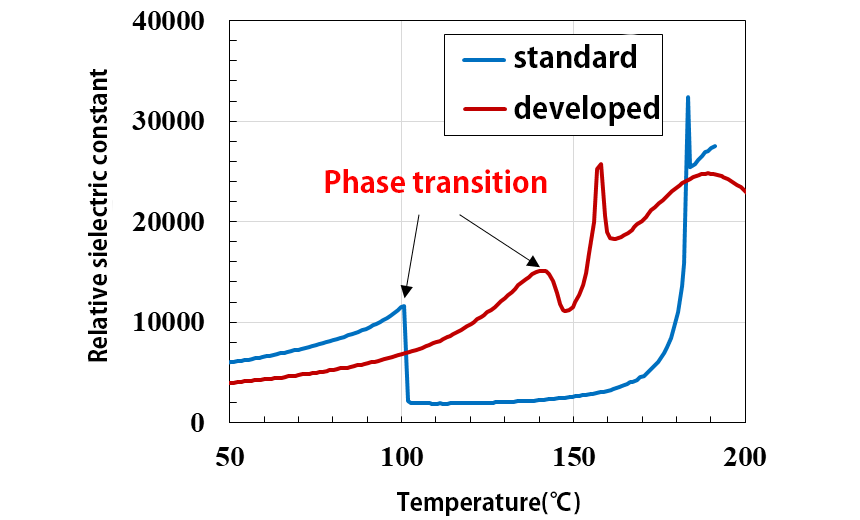
Comparison of temperature dependence of relative dielectric constant
Complex Oxides
High-nickel positive electrode materials for lithium-ion secondary batteries
We have focused our research and development on high-nickel positive electrode materials capable of achieving high energy density. The newly developed 721NT has 12% improved capacity while maintaining the same lifetime as our commercial product 503LP. We are also developing additional high-capacity products, high-voltage products and cobalt-free products to meet our customer needs by controlling the composition and shape of the materials.
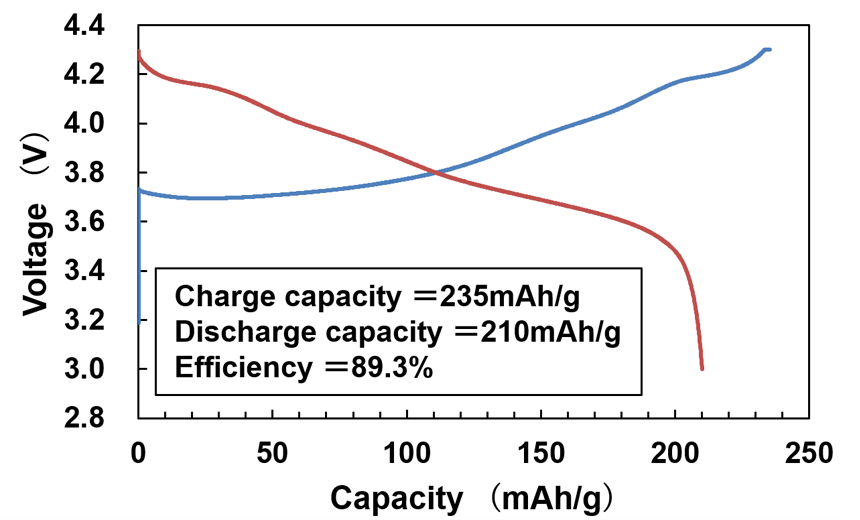
Capacity characteristic of 721NT
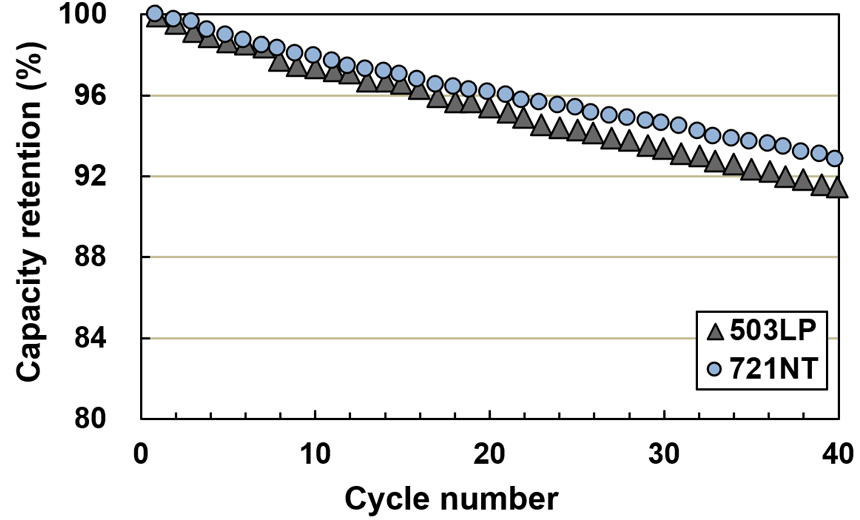
Cycle characteristic of 721NT
ZnO Nanoparticles
We are developing ZnO nanoparticles with application to electronic components in mind. ZnO particles with characteristic shapes such as acicular, hexagonal plate and spherical can be synthesized by wet synthesis methods. Spherical nanoparticles with high packing density in which minute components are uniformly added in molecular size are expected to be applied to sensors and varistors.
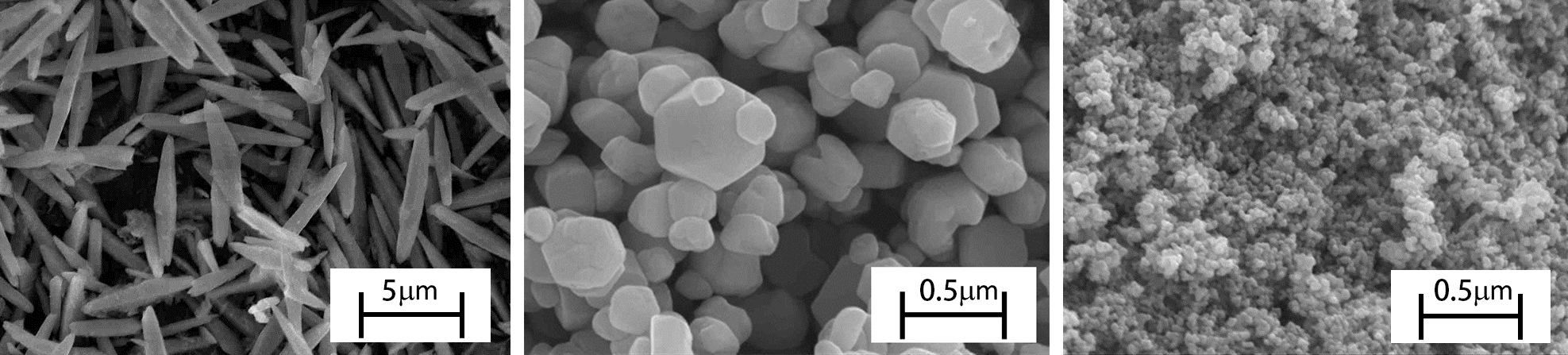
Scanning electron micrographs of zinc oxide nanoparticles
Basic Zinc Salts / RIPROZ® and Synthetic Hydrozincite
RIPROZ® (simonkolleite, basic zinc chloride) is a sustained-release zinc hydroxide that dissolves zinc ion in moist environments for a longer period of time than other zinc salts. Professor Yamamoto's laboratory at Yamagata University has shown in animal studies that RIPROZ® has wound healing effects. This is thought to be due mainly to long-term activation of skin regeneration factors such as proteolytic enzyme by zinc ions. RIPROZ® has been put into practical use as an additive in hair tonic. We are also developing a basic zinc carbonate, hydrozincite, with a sustained-release function of zinc ion, which is expected to be applied to bone regeneration treatment.
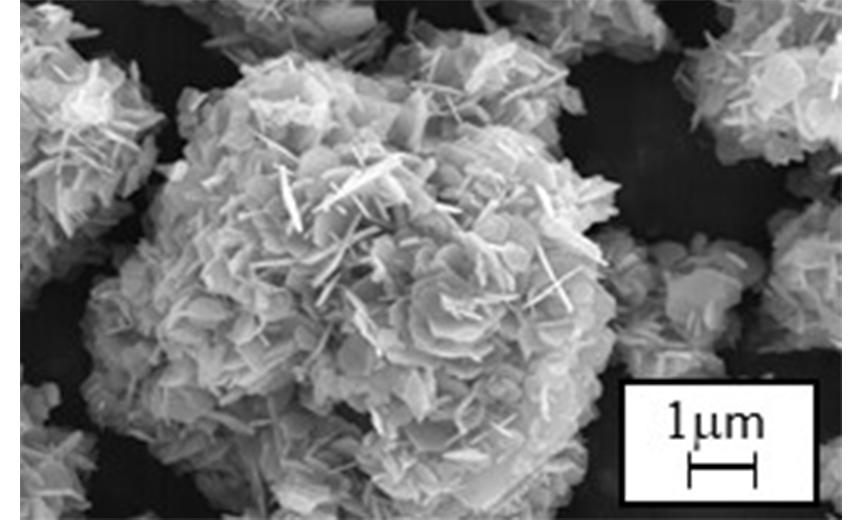
Scanning electron micrograph of RIPROZ®
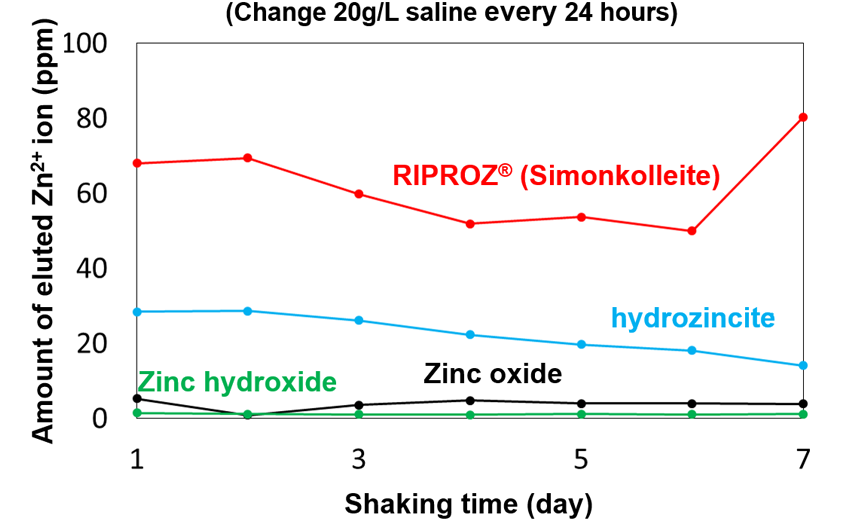
Sustained-release of Zn2+ions from basic zinc salts
Granular Halloysite
Halloysite is an aluminosilicate clay mineral with the empirical formula Al2Si2O5(OH)4. Granular halloysite is a micron-sized spherical granule made of high-purity halloysite nanotubes. Some potential applications include catalysts, deodorants, adsorbents and antibacterial agents.
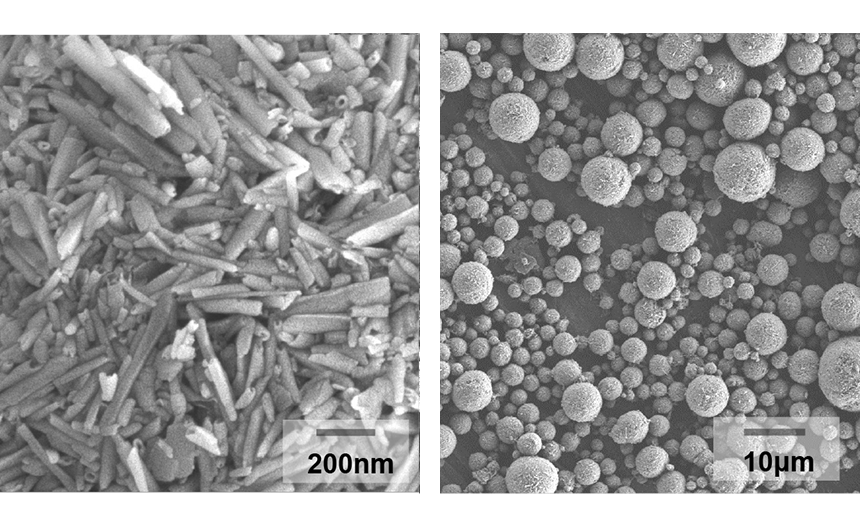
Scanning electron micrographs of Granular halloysite
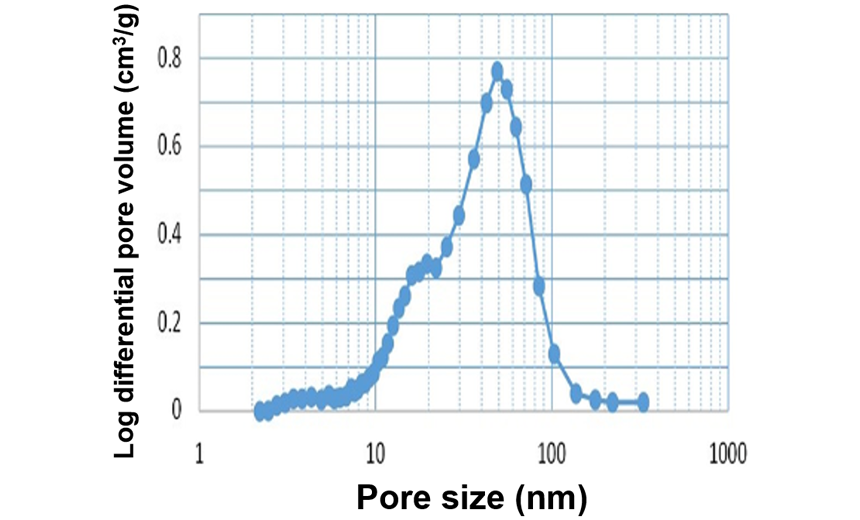
Pore size distribution of Granular halloysite

